You may occasionally feel chilly during a fast and have cold fingers and toes. Most people think they feel cold because they aren’t supposed to eat during the fasting window. It’s somehow related, but more science-based facts explain why fasting makes someone colder.
Fasting makes you colder because you’re in a fasted state with no ingestion of food that keeps you warm through digestion. Also, the blood flow to your fat deposits increases as the body burns fat as fuel to produce the heat required to protect the vital organs.
An underlying illness or low blood sugar could also be the reason. Continue reading to understand all the facts on why fasting makes you colder. I’ll also give you several tips on how to stop feeling cold while fasting.

Coldness Is a Side Effect of Fasting
With intermittent fasting, you can experience several side effects, such as hunger, fatigue, and moodiness, because of changing your eating habits. However, one of the biggest concerns with fasters is feeling colder than usual.
Let’s look at the facts on why fasting makes you colder.
Eating Fewer Calories
Most people think intermittent fasting is about eating the least calories possible to lose weight.
However, too much calorie reduction means your body will lack enough fuel (food) to produce heat. You may feel significantly colder during the fasting window due to less heat production after consuming less food or calories in your eating window.
Additionally, eating too few calories can be more detrimental to your health than beneficial because dropping weight too quickly can have negative long-term implications like muscle loss and nutrient deficiencies.
So, ensure you’re eating enough calories to get you through your entire fasting window, depending on the type of intermittent fasting you’re following. Use a calorie counter to determine the precise amount of maintenance calories your body requires to remain fasted.
Loss of Body Fat
The primary goal of fasting is to lose excess body fat and maintain a lean body mass over time.
So, you’ll likely feel colder when fasting because your body sheds a lot of fat, which also acts as insulation. Body fat also cushions your vital organs and acts as an energy source when blood glucose levels are low.
With prolonged fasting, you can expect to lose a significant amount of body fat as your body converts the stored fat into fuel to use as energy for maintaining vital body functions.
There is no way out of this unless you stop intermittent fasting to prevent losing fat. So, it’s normal to feel colder when fasting because you’re in a fat-burning phase and shedding more body fat than usual.
Low Blood Sugar
When you skip meals for extended periods, your blood sugar levels may drop, which signals your body to find another energy source since glucose is the primary fuel for most bodily functions.
Although low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, mainly causes sweating when fasting, it can also make you feel colder as your body experiences hunger pangs and shock.
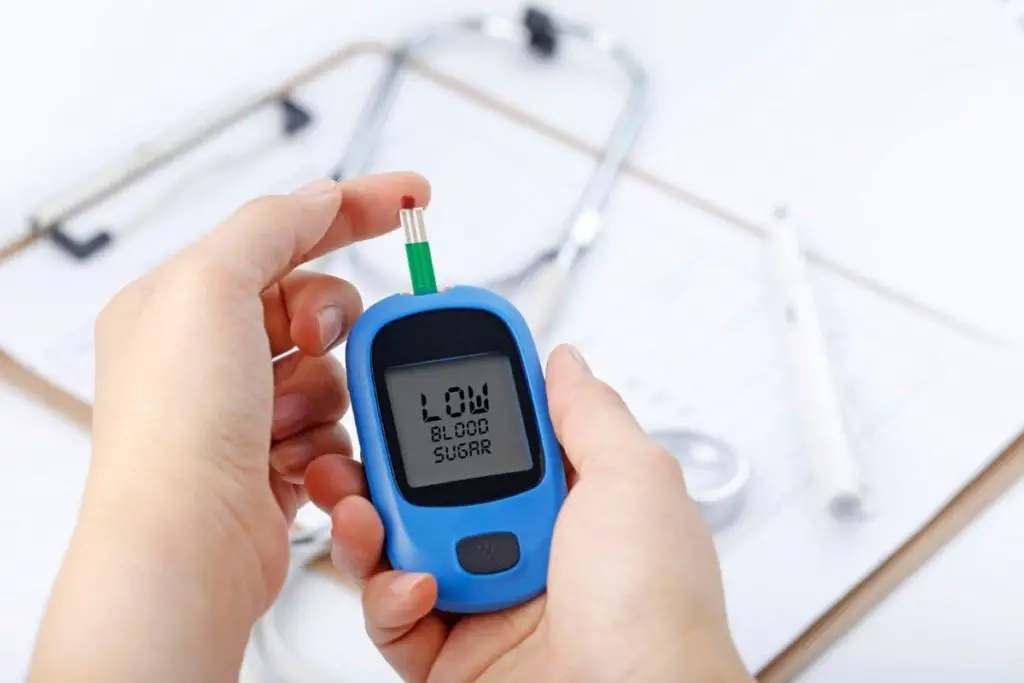
The following are some of the common symptoms of low blood sugar.
- Tingling or numbness of the mouth
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Confusion
Keep an eye out for hypoglycemia symptoms since if it isn’t treated or controlled for a long time, it can cause unconsciousness, seizures, or death. So, if you’ve been fasting for a long time, you can visit your doctor or have a blood glucose test to see if you have hypoglycemia or not.
Poor Blood Circulation
Cold hands or feet during fasting may indicate poor blood circulation in those particular body parts. It can also indicate redirection of blood flow to fat deposits, causing your hands or feet to receive less blood and feel cold.
According to a 2010 study on adipose tissue flow, researchers found that your blood flow changes during extended fasting. It moves towards your fat stores, and helps convert stored fat into fuel.
As a result, it’s normal to feel colder following an extended fast, but you should perform it under a doctor’s supervision to ensure your vitals are functioning properly.
However, severe cases can signal underlying heart diseases, such as peripheral artery disease and Raynaud’s phenomenon. Therefore, you should consult your doctor immediately after a prolonged period of coldness or numbness in your hands or feet.
Underactive Thyroid
A 2014 study found that fasting causes the thyroid gland to generate less of the thyroid hormones needed to control metabolism and body temperature, leading to a condition known as hypothyroidism.
As a result, an underactive thyroid can make you feel constantly cold when fasting because it lowers your metabolism and disrupts the functioning of your body’s organs, such as the heart, brain, and muscles leading to low body temperatures.
You must see a doctor immediately if you notice serious symptoms like dry skin and thinning hair.
Low Iron Levels
Another possible reason why you could be experiencing cold temperatures during fasting is low iron levels in the body. Iron deficiency (anemia) causes a drop in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen through the bloodstream.
Other severe signs of anemia or low iron levels, in addition to feeling chills, include the following:
- Paleness on the skin, gums, lower eyelid, and nail bed.
- Dizziness or weakness.
- Breathing difficulty.
- Restless leg syndrome.
It would be best to talk with your doctor about the appropriate iron supplements or dietary modifications to avoid being eventually diagnosed with anemia.
Tips on How To Stop Feeling Cold While Fasting
The first step you should take when you’re frequently feeling cold during fasting is to speak with your doctor. However, there are several tips you can use to prevent feeling cold without stopping your intermittent fasting journey halfway.

Here are the tips on how to stop feeling cold while fasting.
- Drink hot and unsweetened black coffee or green tea.
- Consume vegetable or chicken soup.
- Eat enough maintenance calories in your eating window.
- Do light exercises regularly, but in short intervals.
- Avoid consuming cold foods and beverages.
- Take a hot bath.
- Wear warm clothes
- Take supplements, especially if your iron levels are low.
Conclusion
When you’re in a fasted state, you tend to feel colder due to low body temperature resulting from consuming less food. Also, a lack of glucose leads to more blood flow into your fat stores for energy production than other body parts. Therefore, it’s perfectly normal to feel colder when fasting, but you can mitigate this by trying the above warm-up tips.

